
Operating expenses, commonly abbreviated as Op Ex, are the routine bills and costs you regularly face—like paying your staff, renting office space, or paying for electricity and internet. Understanding your Op Ex is important to determine your company’s financial health and influence critical business decisions. For accounting purposes, business expenses are recorded on the profit and loss (or income) statement and subtracted from revenue to arrive at a business’ net profit or loss. If they meet the IRS definition of ordinary and necessary, business expenses can be either fully or partially deducted from revenue, which will reduce a company’s taxable income and tax liability. Interpreting the operating expense ratio requires considering industry-specific benchmarks, as cost structures vary significantly by sector. Manufacturing firms, for example, typically have higher fixed costs than tech startups, influencing their respective OER norms.
Subscribe to Taxfyle
Operating expenses fundamentally shape a business’s financial health through their direct impact on profitability. Each dollar an organization saves when they reduce operating expenses flows straight to the bottom line, enhancing profit margins without requiring additional sales efforts. This explains why businesses with similar revenue figures can experience vastly different profit outcomes. Operating expenses are the day-to-day costs that businesses incur to keep their operations running, distinct from the costs directly tied to producing goods or services.
- This helps ensure that their offices, equipment, and other essential assets remain in optimal condition.
- A well-structured Excel or Google Sheets template works effectively when designed with clear categories and consistent formatting.
- Cost of goods sold, or COGS, is a term meaning the direct expenses related to the production of items an entity sells.
- Companies also incur operating expenses for regular legal services, such as regulatory compliance, dispute resolutions, intellectual property protection, and contract drafting.
- When you manage operating expenses effectively, you create a clear path to business success through improved margins, competitive pricing, and financial stability.
- Generally, businesses can deduct operating expenses in the year they were incurred.
Manufacturing and Production Costs
- Bookkeepers record operating expenses as expense accounts in journal entries.
- When wages are paid on a productivity basis, such as piecework or incentive compensation, these costs can be characterized as semi-variable since they have both fixed and variable components.
- Manufacturing firms, for example, typically have higher fixed costs than tech startups, influencing their respective OER norms.
- This knowledge will help you identify areas for cost optimization, improve profitability, and make strategic decisions to drive your company’s growth.
- Capital expenditures for long-term assets appear on the balance sheet rather than the income statement.
From the rent paid for office space to the salaries of employees, these ongoing costs are essential for keeping the wheels of a business turning smoothly. It’s important to note that the principle of economies of scale is limited past contra asset account a certain point. For example, a company can only increase production so much in a single factory. At some point, it will need to expand to a second factory to keep growing, which would then increase its fixed costs. Businesses must balance keeping their operating costs low while allowing it to grow and increase sales.
Operating vs. non-operating expenses in financial statements
This information is provided for informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal, financial, or tax advice. Readers should contact their attorneys, financial advisors, or tax professionals to obtain advice with respect to any particular matter. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. For each period, we can project the OpEx value by multiplying the “% Revenue” assumption by the revenue amount in the matching period, as shown in the screenshot above.

- You can identify your operating expenses in several ways, such as by using software, by working with a professional, or by listing them with a pen and paper.
- These models can account for factors like expected business growth, inflation, and planned initiatives.
- Organizing operating expenses well also aids in using financial resources wisely, helping you enhance the cash flow management.
- If a company lays off three out of four customer service employees, payroll expenses will drop, leading to immediate savings while increasing short-term profits.
- Expenses can be divided into several different types, including equipment costs, inventory, and facilities costs.
- These expenses can be more challenging to predict accurately, as they change in proportion to your business operations.
Even basic accounting software can pay for itself by helping you spot financial issues faster and making tax preparation easier. Now that you understand what operating expenses are and how to track them, let’s focus on practical ways to manage and reduce these costs. Small changes in how you handle expenses can improve cash flow and lead to big improvements in your QuickBooks ProAdvisor bottom line. Here are five proven strategies that can help any business spend smarter and move faster.

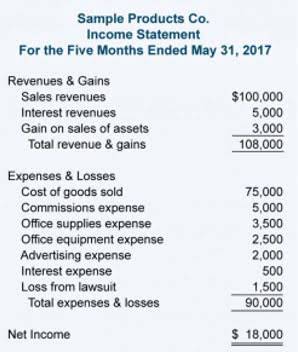
Alternative Method: Using the Income Statement
However, they also require closer monitoring to ensure they don’t spiral out of control during busy periods. Because they are a financial expense that does not directly contribute to selling services or products, they aren’t considered assets. Cost of Goods Sold refers to costs directly related to the production of your goods or service, including raw materials and labor costs. It is critical to note that operational activities differ greatly among industries. A business activity can be classified as operational in one industry, but financing or investing in another. For instance, buying a building is typically an investing activity in most industries.

At the end of your accounting period, separate your operating expenses from other types of expenses. You’ll business operating expenses then use the formula described in the following section to calculate your operating expenses. Unlike direct production costs, these expenses support the ongoing administrative and functional needs of your company, ensuring smooth operational continuity and efficiency.
